NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination (PDF Download)
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination are provided here in a clear, accurate, and exam-oriented format. This resource is specially designed to help Class 10 students understand all key concepts related to control and coordination in living organisms as per the latest CBSE syllabus 2025–26.
In this article, you will get detailed, step-by-step answers to all questions from NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7. Each solution is prepared strictly according to NCERT guidelines, making it ideal for board exam preparation, school assignments, and regular practice.
Students can also find important extra questions with answers, which are frequently asked in CBSE and State Board examinations. These solutions help improve conceptual clarity and boost confidence while writing answers in exams.
✅ Free PDF Download Available
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination PDF (English Medium) absolutely free.
This study material is useful for students of:
CBSE Board, Karnataka Board (SSLC), Bihar Board, Uttarakhand Board, MP Board, Gujarat Board
These solutions are fully compatible with NCERT textbooks and Karnataka State Board books, strictly following the updated CBSE curriculum for the academic session 2025–26.
If you are looking for reliable NCERT solutions, exam-oriented answers, and high-quality PDF notes for Class 10 Science, this post will serve as a complete one-stop solution.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination
Complete NCERT Answer Guide (CBSE 2025–26)
Control and Coordination is one of the most important biology chapters in Class 10 Science. This chapter explains how living organisms respond to different stimuli and maintain balance within the body. The content given here is fully original, exam-oriented, and prepared according to the latest NCERT syllabus for the academic year 2025–26.
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 are useful for board exam preparation, revision before tests, and completing school assignments accurately.
What is Control and Coordination?
Control and coordination refer to the way in which different activities of the body are regulated and integrated. Living organisms continuously receive information from their surroundings and respond appropriately to survive. This coordination is essential for proper functioning of organs and systems.
In humans and animals, control and coordination are mainly achieved through the nervous system and hormones, whereas in plants, coordination occurs through chemical substances.
Nervous System in Animals
The nervous system is responsible for quick communication within the body. It helps animals respond rapidly to changes in the environment.
Functions of the Nervous System
Receives information from sense organs
Transmits signals through nerves
Produces responses by activating muscles or glands
The nervous system works through electrical impulses that travel along nerve cells.
Reflex Action:-
A reflex action is a fast and automatic response to a stimulus. It does not require conscious thinking. Reflex actions are mainly protective in nature.
Characteristics of Reflex Action
Occurs instantly
Controlled by the spinal cord
Involuntary response
Protects the body from sudden danger
Example: Withdrawal of hand after touching a hot object.
Human Brain and Its Functions
The brain is the control center of the nervous system. It receives information, processes it, and sends instructions to different parts of the body.
Major Parts of the Brain
Forebrain: Responsible for thinking, memory, and emotions
Midbrain: Controls visual and auditory reflexes
Hindbrain: Maintains balance, posture, and involuntary activities
The brain plays a key role in voluntary actions such as walking, writing, and speaking.
Difference Between Reflex Action and Voluntary Action
Reflex actions happen automatically without thinking, while voluntary actions are performed consciously. Voluntary actions are controlled by the brain and can be modified according to the situation.
Walking is an example of a voluntary action because the brain decides when and how the movement should take place.
Coordination in Plants
Plants do not have a nervous system, yet they respond to environmental changes. These responses are controlled by chemical substances called plant hormones.
Types of Plant Movements
Directional movements: Response depends on the direction of the stimulus
Non-directional movements: Response does not depend on stimulus direction
Plant Hormones (Phytohormones)
Plant hormones are chemical messengers that control growth and responses in plants.
Important Plant Hormones
Auxins: Promote cell elongation
Gibberellins: Stimulate stem growth
Cytokinins: Promote cell division
Abscisic acid: Inhibits growth
Ethylene: Controls fruit ripening
Hormonal Control in Animals
Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands directly into the bloodstream. They regulate growth, metabolism, and development.
Endocrine Glands in Humans
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Pancreas
Gonads
Each gland secretes specific hormones that act on target organs.
Difference Between Nervous and Hormonal Control
Nervous control is fast and short-lived, whereas hormonal control is slow but long-lasting. Nervous signals travel through nerves, while hormones are transported through blood.
Importance of Control and Coordination
Maintains balance inside the body
Helps organisms adapt to surroundings
Ensures proper functioning of organs
Essential for survival
NCERT Intext Questions – Chapter 7
Page 119
Question1: What is the difference between reflex action and walking?
Answer:
A reflex action is an automatic response that occurs without conscious effort and is controlled by the spinal cord. Walking, however, is a conscious activity that involves decision-making by the brain and is therefore considered a voluntary action.
Q1. Explain how information is transmitted at the synapse between two neurons.
Answer:
In the nervous system, nerve cells do not remain directly attached to each other. The tiny gap present between two consecutive neurons is known as a synapse. When a nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon of the first neuron, it does not jump directly to the next neuron. Instead, specific chemical messengers are released at the axon terminal. These chemicals travel across the synaptic gap and stimulate the dendrite of the following neuron. This process ensures smooth transmission of messages throughout the nervous system.
Q2. Which part of the human brain helps in maintaining balance and body posture?
Answer:
The cerebellum, which is located at the back of the brain, plays a major role in maintaining balance, posture, and coordination of voluntary movements. It helps the body perform precise and controlled muscular actions.
Q3. Describe how humans are able to sense the fragrance of an incense stick.
Answer:
The fragrance released by an incense stick spreads in the surrounding air. When a person breathes in, these smell particles enter the nasal cavity and stimulate the olfactory receptors present there. These receptors send signals through sensory nerves to a specific region of the forebrain. The brain then interprets these signals, allowing us to recognize the smell.
Q4. What role does the brain play in reflex activities?
Answer:
Reflex actions occur without the direct involvement of the brain. Such responses are quick and automatic, mainly controlled by the spinal cord. Although the brain is informed after the action has occurred, it does not participate in taking immediate decisions during reflex activities.
Plant Hormones and Movements in Plants
Q5. What are plant hormones? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Plant hormones, also called phytohormones, are chemical substances produced in plants in very small quantities. They regulate various physiological activities such as growth, development, flowering, ripening of fruits, and responses to environmental changes. Important plant hormones include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene.
Q6. How is the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot toward light?
Answer:
The movement seen in the leaves of a sensitive plant occurs due to touch and does not depend on the direction of the stimulus. This type of movement is temporary and results from changes in water pressure within cells rather than growth. On the other hand, the bending of a shoot towards light depends on the direction of the stimulus. It is a permanent movement caused by unequal growth on different sides of the shoot.
Q7. Name a plant hormone that supports growth.
Answer:
Auxin is a plant hormone that promotes cell elongation and helps in the growth of plant parts.
Q8. Explain the role of auxins in helping tendrils coil around a support.
Answer:
When a tendril comes into contact with a support, auxins shift away from the side touching the object and accumulate on the opposite side. Since auxins promote growth, the side with a higher concentration of auxins grows more rapidly. This uneven growth causes the tendril to bend and coil around the support, providing stability to the plant.
Q9. Describe an activity to demonstrate hydrotropism in plants.
Answer:
To show hydrotropism, take two containers filled with soil and plant a seedling in each. Water the soil regularly in the first container. In the second container, place a porous pot filled with water inside the soil, but do not water the soil directly. After a few days, the roots of the seedling in the second container will bend toward the source of water, proving that roots grow in the direction of moisture.
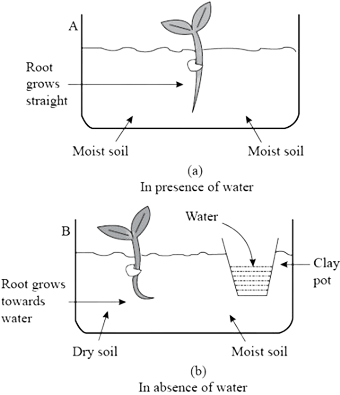
Diagram showing hydrotropism in plant roots (for educational purpose).
✅ Class 10 Science – Chapter 7: Control and Coordination
Page 125 + Chapter-End Questions
Q1. How does chemical coordination Occur in animals?
Answer:
Animals maintain chemical coordination through hormones produced by the endocrine glands. These glands releases hormones directly into the bloodstream and . The blood then carries these hormones to specific body parts where special receptor cells receive the signal. Once the hormone reaches its target, the cells are respond by performing the required function. Together with the nervous system, this hormonal system helps regulate growth, metabolism, emotions, and several body functions.
Q2. Why is a use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:
Iodised salt is important because the thyroid gland requires iodine to form the hormone thyroxine. This hormone manages several metabolic processes of the body. If the body does not get enough iodine, and thyroid fails to produce thyroxine properly,which can lead to a disorder known as goitre. Therefore,using of iodised salt prevents such health issues.
Q3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is released into the blood?
Answer:
When adrenaline is released during stress, fear, or danger, the body becomes alert and ready for quick action. Heartbeat becomes faster, supplying extra oxygen to the muscles. Blood flow decreases toward the skin and digestive organs and increases toward the limbs. Breathing rate also rises due to rapid movement of diaphragm and chest muscles. These changes collectively prepare the body for immediate reaction.
Q4. Why are some diabetic patients treated with insulin injections?
Answer:
The hormone insulin helps in controlling the amount of glucose present in the blood. If a person’s body does not produce enough insulin, their blood sugar level increases dangerously. To maintain a normal level of blood sugar and avoid complications, diabetic patients are given insulin injections.
Q1. Which of the following is an plant hormones ?
(d) Cytokinin
Q2. The gap between two neurons is called:
(b) Synapse
Q3. The brain is responsible for:
(d) All of the above (ALL)
Q4. What is the function of receptors in our body? What happened if they do not work properly?
Answer:
Receptors are specialised cells present in sense organs such as eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue. Their job is to detect changes in the environment and send messages to the brain or spinal cord. If receptors become damaged or stop functioning, the body will not sense external stimuli correctly. As a result, the person may fail to react on time. For example, if skin receptors are not working, a person may not feel heat from a hot object and may get burned.
Q5. Draw a neuron and explain its function.
Answer:
A neuron is the basic unit of the nervous system and is made up of three major parts:
• Cell Body – contains the nucleus and cytoplasm.
• Dendrites – receive signals from other neurons.
• Axon – carries messages away from the cell body.
Function:
Neuron carries message in the form of electrical impulses. They pass information from sense organs to the brain and spinal cord and from the brain to different parts of the body.
Q6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer:
Phototropism refers to the bending of plant parts in response to light. Shoots grow towards light (is known as positive phototropism) while roots grow away from it (is known as negative phototropism). This happens because the hormone auxin gathers on the darker side of the plant. The cells on the darker side grow faster, causing the shoot to bend towards the source of light.
Q7. Which signals are disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer:
A spinal cord injury interrupts the flow of signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Reflex actions, which normally occur through the spinal cord, may stop or slow down. Many involuntary actions may also become irregular due to this disruption.
Q8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer:
Plants use plant hormones to coordinate growth and responses. Hormones like auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid are produced in actively growing regions. These hormones travel to other parts of the plant and help it react to light, gravity, injury, shortage of water, and other environmental changes.
Q9. Why does an organism require a system of control and coordination?
Answer:
Organisms need control and coordination to:
• Adjust to environmental changes
• Manage voluntary and involuntary activities
• Maintain internal stability
• Think, learn, and respond properly
Without this system, the body cannot function in an organized and balanced way.
Q10. Difference between involuntary actions and reflex actions
Involuntary Actions Reflex Actions
Occur without conscious effort. Automatic and immediate response to a stimulus.
Controlled by the midbrain and hindbrain. Controlled mainly by the spinal cord.
Example: heartbeat, breathing. Example: blinking, pulling hand away from heat.
Q11. Compare nervous and hormonal mechanisms in animals.
Nervous System Hormonal System
Works rapidly. Works slowly.
Uses electrical impulses. Uses chemical messengers.
Produces short-term effects. Produces long-lasting effects.
Does not control growth. Influences growth and metabolism.
Q12. Difference between movement in a sensitive plant and movement in human legs
Sensitive Plant Human Leg Movement
Responds to touch. Controlled by brain and spinal cord.
Movement occurs due to change in water content of cells. Movement occurs by muscle contraction.
Not a voluntary process. A voluntary action.
called as nastic movement. Part of voluntary nervous system.
Control and Coordination Class 10 – Complete Notes, HOTS, NCERT Solutions.
Control and Coordination in plants and animals is an important topic in Class 10 Science Chapter 7. This chapter explains how organisms sense changes in their surroundings and respond to them. It also covers nervous system, hormones, reflex action, plant hormones, and tropic movements.
Below is a fully original and easy-to-understand article covering all important questions and concepts.
What Is Control and Coordination?
Control and coordination is the process through which different parts of an organism work together efficiently.
In animals, it is done by the nervous system and endocrine (hormonal) system.
In plants, it takes place through tropic movements and plant hormones.
⭐ Control and Coordination Class 10 – HOTS Questions and Answers
Q1. What type of plant movement is seen in the coiling of a tendril? How do auxins help in this?
Answer:
The coiling of a tendril shows thigmotropism, a movement caused by touch or contact.
When a tendril touches a support, the side in contact receives less auxin, while the opposite side receives more auxin.
The side with more auxin grows faster, causing the tendril to bend and coil around the support.
Q2. Identify the parts A and B in the dorsal view of the thyroid gland.
Answer:
A – Thyroid gland
B – Parathyroid glands
Q3. Which hormones help in milk production and ejection in mothers?
Answer:
Prolactin – Helps in the production of milk.
Oxytocin – Helps in the ejection (release) of milk.
Q4. How does the pancreas maintain blood glucose levels?
Answer:
The pancreas produces two important hormones:
Insulin helps decrease the blood sugar level by changing extra glucose in the bloodstream into glycogen for storage.
Glucagon – Raises blood sugar by converting glycogen back to glucose.
Together, they keep the blood glucose level balanced.
Q5. What is the pregnancy hormone? Why is it called so?
Answer:
Progesterone is known as the pregnancy hormone.
It maintains pregnancy by:
preventing the formation of new ova
thickening and nourishing the uterine lining
supporting embryo implantation
Q6. What is dormin?
Answer:
Dormin is another name for Abscisic Acid (ABA).
It induces dormancy in seeds and buds.
⭐ Neuron – Structure and Functions
Q7. Answer the following about the neuron diagram:
A – Dendrite
B – Axon
Functions:
Dendrites receive information.
The pathway of a nerve impulse in a neuron begins at the dendrites, passes through the cell body, and continues along the axon for further transmission.
At the synapse, electrical impulse changes into a chemical signal to transmit to the next neuron.
Thyroid Hormone
Thyroxine – Controls metabolism, energy use, body temperature, and development.
Using iodised salt helps the thyroid to make thyroxine properly.
⭐ Plant Hormones – Important Points
A. Types of Plant Hormones (Phytohormones)
Auxin – Promotes growth
Gibberellins – Growth-promoting
Cytokinins – Promote cell division
Abscisic Acid (ABA) – Inhibits growth, causes dormancy
B. Brain Parts and Their Functions
Pons: Controls breathing rhythm
Medulla: Controls involuntary reflexes like heartbeat and respiration
Cerebellum: Maintains balance and coordinates movements
⭐ Value-Based Questions
Q1. How do tendrils find support without sensory organs?
Tendrils perform a movement called circumnutation, where they move in circles.
When they touch a support, one side grows slower and the other grows faster, causing the tendril to coil around it.
Q2. Which system controls internal organs automatically?
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Works without thinking
Has two parts: Sympathetic & Parasympathetic systems
Q3. Why do we sweat during exercise?
It is a reflex action controlled by the nervous system.
Sweating helps to cool the body when temperature rises.
Q4. How can switching on a night bulb every day affect mood?
Low light at night reduces melatonin secretion.
Melatonin controls sleep, mood, immunity, and body rhythms.
Less melatonin → disturbed sleep → mood changes.
⭐ NCERT Solutions (Short Answers)
Q1. What is the function of receptors?
Receptors detect specific stimuli:
Gustatory receptors – taste
Olfactory receptors – smell
Q2. How does a neuron work?
Dendrites receive information
Electrical impulse travels through the neuron
At synapse, chemicals transmit the impulse to the next cell
Q3. What is phototropism? Explain Darwin’s experiment.
Phototropism – movement towards light.
Darwin discovered that:
The tip of the plant detects light
The lower region bends
Removing or covering the tip prevents bending
This proved that the tip sends a growth-regulating signal (auxin) to the lower part.
👉 SSLC 10ನೇ ತರಗತಿ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಸಂಬಂಧಿಸಿದ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಅಧ್ಯಾಯಗಳ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಇಲ್ಲಿ ಲಭ್ಯ:
10th Science Complete Notes
👉10ನೇ ತರಗತಿ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ 13 ನೋಟ್ಸ್ | ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಾಹದ ಕಾಂತೀಯ ಪರಿಣಾಮಗಳು
